Category: Planning
State of Good Repair Resource Requirements Assessment
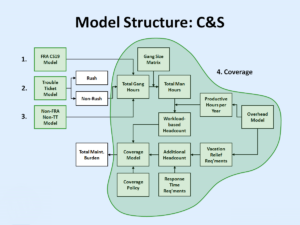 On behalf of a major regional passenger rail operator, as part of ongoing efforts to rightsize the Maintenance of Way (MOW) workforce, we led a team of production planners and analysts to conduct a zero-based budget assessment in all major MOW areas at the maintenance headquarters, gang, shift, and craft levels. In this study, we enumerated each railway infrastructure system that must be maintained by MOW personnel, including periodic and preventative (FRA, FTA, and non-regulatory) maintenance plans for each system, and determine the repair maintenance workload based on both historical trouble ticket data as well as asset quantities and probabilities of failure. We also included major repair workloads for such unforeseen situations as cable degradation, grade crossing accidents, long-term concrete and steel degradation, and interactions between asset renewal activities in the C&S, Track, and Power depts. The study recommended changes in personnel strength in a number of key crafts at several locations, to reduce overtime requirements, ensure that major project backlogs can be addressed in an efficient manner, and to provide preventative maintenance for new assets expected to be commissioned following major capital investment projects.
On behalf of a major regional passenger rail operator, as part of ongoing efforts to rightsize the Maintenance of Way (MOW) workforce, we led a team of production planners and analysts to conduct a zero-based budget assessment in all major MOW areas at the maintenance headquarters, gang, shift, and craft levels. In this study, we enumerated each railway infrastructure system that must be maintained by MOW personnel, including periodic and preventative (FRA, FTA, and non-regulatory) maintenance plans for each system, and determine the repair maintenance workload based on both historical trouble ticket data as well as asset quantities and probabilities of failure. We also included major repair workloads for such unforeseen situations as cable degradation, grade crossing accidents, long-term concrete and steel degradation, and interactions between asset renewal activities in the C&S, Track, and Power depts. The study recommended changes in personnel strength in a number of key crafts at several locations, to reduce overtime requirements, ensure that major project backlogs can be addressed in an efficient manner, and to provide preventative maintenance for new assets expected to be commissioned following major capital investment projects.
Related Publications/Presentations:
Clearance Inventory and Planning for Double-Deck Passenger Equipment
 On behalf of a major passenger transport agency, we convened and progressed a clearance inventory project that aimed to provide a clear path for bi-level passenger coaching stock to enter a major downtown terminal through legacy tunnel infrastructure. This project involved multiple engineering areas and outside consultants, as it was necessary to examine the issue in an interdisciplinary way. The project team explored various approaches to make the car fit, including chamfering existing rolling stock designs, making minor and structural modifications to tunnel infrastructure, introducing speed restrictions as to reduce vehicle dynamic envelope, and upgrading track class to reduce maintenance tolerance. We also procured new clearance modelling software that enabled in-house engineering staff to manipulate LiDAR data and develop their own simulations of various clearance scenarios. Various operational and infrastructure changes required to support daily operation of higher rolling stock were identified by the project. This project is currently in full-scale physical testing based on a proposed car outline.
On behalf of a major passenger transport agency, we convened and progressed a clearance inventory project that aimed to provide a clear path for bi-level passenger coaching stock to enter a major downtown terminal through legacy tunnel infrastructure. This project involved multiple engineering areas and outside consultants, as it was necessary to examine the issue in an interdisciplinary way. The project team explored various approaches to make the car fit, including chamfering existing rolling stock designs, making minor and structural modifications to tunnel infrastructure, introducing speed restrictions as to reduce vehicle dynamic envelope, and upgrading track class to reduce maintenance tolerance. We also procured new clearance modelling software that enabled in-house engineering staff to manipulate LiDAR data and develop their own simulations of various clearance scenarios. Various operational and infrastructure changes required to support daily operation of higher rolling stock were identified by the project. This project is currently in full-scale physical testing based on a proposed car outline.
Business Case for Friday Exception Schedules in Urban Transit
 For a major regional transit authority, we developed a strategic business case for providing separate baseline schedules on Fridays distinct from other weekdays due to significantly different time-of-day and geographical ridership patterns. At that time, regular commuters were trending towards more flexible work scheduling, telecommuting arrangements, and 4½-day weeks especially in the summer, and we observed from Automated Fare Collection (AFC) data that the gaps between midweek and Friday ridership have widened. These Friday exception schedules are not unusual: transit operators ran full Saturday lunchtime rush-hours in the interwar years, while private bus companies, airlines, and freight railroads operate many exceptions today. They can help the operator better match service supply to passenger demand. We found through longitudinal analysis of data that more regular commuters skipped Friday’s trip than other weekdays’. Detailed analysis for 14 representative routes revealed 4.7% lower ridership on Fridays, potentially allowing 7.4% reductions in vehicle-hours operated. Available savings were route-specific, with 25% service reductions possible on some, whereas 25% service fortification was required on leisure-heavy routes having increased Friday ridership. We estimated that implementing separate Friday base schedules systemwide could provide an annual surplus of $10~$17 million for reinvestment elsewhere in the network. From a crewing perspective, we found that the resulting reduced Friday crew requirements could lead to an 1.8% increase in desirable weekend-inclusive regular days-off rosters, and 2.4% reduction in non-preferred midweek days-off rosters. Our recommendation was for the continued implementation of a computerized run-cutting system, and creation of routine analytical processes for multi-variate ridership analysis allowing differences across days, routes, time periods, and other variables to be determined, which together will form the prerequisites for implementing a separate Friday base schedule.
For a major regional transit authority, we developed a strategic business case for providing separate baseline schedules on Fridays distinct from other weekdays due to significantly different time-of-day and geographical ridership patterns. At that time, regular commuters were trending towards more flexible work scheduling, telecommuting arrangements, and 4½-day weeks especially in the summer, and we observed from Automated Fare Collection (AFC) data that the gaps between midweek and Friday ridership have widened. These Friday exception schedules are not unusual: transit operators ran full Saturday lunchtime rush-hours in the interwar years, while private bus companies, airlines, and freight railroads operate many exceptions today. They can help the operator better match service supply to passenger demand. We found through longitudinal analysis of data that more regular commuters skipped Friday’s trip than other weekdays’. Detailed analysis for 14 representative routes revealed 4.7% lower ridership on Fridays, potentially allowing 7.4% reductions in vehicle-hours operated. Available savings were route-specific, with 25% service reductions possible on some, whereas 25% service fortification was required on leisure-heavy routes having increased Friday ridership. We estimated that implementing separate Friday base schedules systemwide could provide an annual surplus of $10~$17 million for reinvestment elsewhere in the network. From a crewing perspective, we found that the resulting reduced Friday crew requirements could lead to an 1.8% increase in desirable weekend-inclusive regular days-off rosters, and 2.4% reduction in non-preferred midweek days-off rosters. Our recommendation was for the continued implementation of a computerized run-cutting system, and creation of routine analytical processes for multi-variate ridership analysis allowing differences across days, routes, time periods, and other variables to be determined, which together will form the prerequisites for implementing a separate Friday base schedule.
Related Publications/Presentations:
Observational Study of Subway Customer Seat Preferences
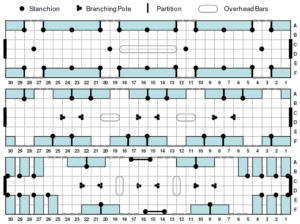 For a major metro system, we performed an observational study of how customers tended to distribute themselves within each vehicle, with a view towards making recommendations about vehicle design (e.g. door, pole, and seat placement), and to reduce station dwell time. The plastic bench seats installed are otherwise highly homogeneous, but we identified special attributes such as adjacency to doors, whether a partition was present, or if the seating was longitudinal, transverse, facing or back to the direction of travel, and discovered patterns in customer seat choice. Results, based on seating- and standing-room occupancy probability statistics, show customers generally prefer seats adjacent to doors, no real preference for seats adjacent to support stanchions, but active disdain for bench spots between two other seats. On cars featuring transverse seating, customers prefer window seats, but have almost equal preference for backward- or forward-facing seats. No demographic differences were found amongst seated passengers, but as load factor increased, men had higher probabilities of being standees compared to women. 90% seat utilization is only achieved at 120% load factor; furthermore, standing customers strongly prefer to crowd vestibule areas between doors (particularly in cars with symmetric door arrangements), and hold onto vertical poles. We recommended that future railcars where possible should ideally be designed with asymmetric door apertures, 2+2+2 partitioned longitudinal seats, and no stanchions or partitions near doorways. This study received substantial attention within the research community and spawned similar studies in other cities of customer seating preferences, including some employing survey and focus group methods, thereby indirectly improving railcar seating layouts in a number of U.S. cities.
For a major metro system, we performed an observational study of how customers tended to distribute themselves within each vehicle, with a view towards making recommendations about vehicle design (e.g. door, pole, and seat placement), and to reduce station dwell time. The plastic bench seats installed are otherwise highly homogeneous, but we identified special attributes such as adjacency to doors, whether a partition was present, or if the seating was longitudinal, transverse, facing or back to the direction of travel, and discovered patterns in customer seat choice. Results, based on seating- and standing-room occupancy probability statistics, show customers generally prefer seats adjacent to doors, no real preference for seats adjacent to support stanchions, but active disdain for bench spots between two other seats. On cars featuring transverse seating, customers prefer window seats, but have almost equal preference for backward- or forward-facing seats. No demographic differences were found amongst seated passengers, but as load factor increased, men had higher probabilities of being standees compared to women. 90% seat utilization is only achieved at 120% load factor; furthermore, standing customers strongly prefer to crowd vestibule areas between doors (particularly in cars with symmetric door arrangements), and hold onto vertical poles. We recommended that future railcars where possible should ideally be designed with asymmetric door apertures, 2+2+2 partitioned longitudinal seats, and no stanchions or partitions near doorways. This study received substantial attention within the research community and spawned similar studies in other cities of customer seating preferences, including some employing survey and focus group methods, thereby indirectly improving railcar seating layouts in a number of U.S. cities.
Related Publications/Presentations:
Transport Equity Analyses for Major Service Changes
 On behalf of a major U.S. public transit agency, we developed analytical methodologies and performed demographic analysis to determine the impact of proposed service changes on protected customer groups (minority and low-income). At that time, a large package of bus service changes was being considered, including changes in service span, route, frequency—which also resulted in specific impacts in load factors, access distance, and other performance metrics that are monitored under the agency’s own service standard and various regulatory requirements. Changes were also proposed for several rail lines. For each proposed service change action, we determined whether it met the “major service change” threshold. If it did, we determined through demographic analysis of likely users as to whether the change impacted the protected groups disproportionately. From these results, the agency was able to modify proposed service changes to avoid impacting protected groups while achieving the required cost reductions. These results were also provided to relevant authorities for establishing Title VI compliance of the service change process.
On behalf of a major U.S. public transit agency, we developed analytical methodologies and performed demographic analysis to determine the impact of proposed service changes on protected customer groups (minority and low-income). At that time, a large package of bus service changes was being considered, including changes in service span, route, frequency—which also resulted in specific impacts in load factors, access distance, and other performance metrics that are monitored under the agency’s own service standard and various regulatory requirements. Changes were also proposed for several rail lines. For each proposed service change action, we determined whether it met the “major service change” threshold. If it did, we determined through demographic analysis of likely users as to whether the change impacted the protected groups disproportionately. From these results, the agency was able to modify proposed service changes to avoid impacting protected groups while achieving the required cost reductions. These results were also provided to relevant authorities for establishing Title VI compliance of the service change process.
Related Publications/Presentations:
Railroad Operations and Alignment Design Support

We provided specialized railroad technical support to a larger planning and engineering team that was performing an environmental impact and alternatives analysis on behalf of a state department of transportation that is contemplating several options for redeveloping a rail corridor for mixed commuter, intercity rail, and freight transportation use. Specifically, we laid out new alignment options at a conceptual engineering level to minimize property takings by re-using existing corridors. The new alignments we identified connected two parallel corridors at strategic locations to enable integrated service plans, to allow freight traffic to be routed onto a by-pass away from urban centres and reduce grade crossing risks. We also developed operating plans to show that overhead freight traffic can be routed through the area without delay while offering a robust schedule for commuter and intercity services operated under various growth scenarios. At this time, the project has been constructed, although with a substantially different form of governance and service plan than what we envisioned.
Note: Alex Lu performed this work as an employee of another firm.
Requirements Documentation for Operations Admin Systems
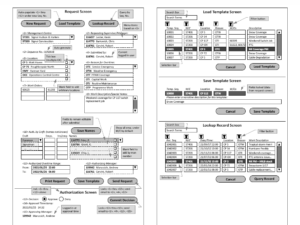 We were tasked by the engineering department of a railroad to provide requirements documents, functional design, process engineering, and project management services for two operations administration systems. The first system dealt with keeping track of position advertisements, displacements, and seniority evaluations for awards in a heavily unionized environment with multiple crafts, physical characteristics qualifications, and concurrent seniorities on multiple rosters due to promotional paths. A legacy system was in place but did not provide all required functionalities. We assessed the current system and worked out the business case for complete replacement on a modernized platform versus incremental improvements. Although an agile process could have reproduced many existing functionalities very quickly, we found that certain signal systems employees had the skills to continue to improve the legacy system, access to the source code, and compilers continued to be supported by the vendor. For all those reasons, we provided project management service to deliver the required improvements using the legacy platform. The second one is used by field supervision to record overtime approvals and provide audit compliance. We worked with subject matter experts, field supervision, and executive groups to determine system requirements and develop a process that captured all necessary information without introducing undue burden on supervisory personnel. The completed project plan was turned over to corporate I.T. and compliance groups for implementation.
We were tasked by the engineering department of a railroad to provide requirements documents, functional design, process engineering, and project management services for two operations administration systems. The first system dealt with keeping track of position advertisements, displacements, and seniority evaluations for awards in a heavily unionized environment with multiple crafts, physical characteristics qualifications, and concurrent seniorities on multiple rosters due to promotional paths. A legacy system was in place but did not provide all required functionalities. We assessed the current system and worked out the business case for complete replacement on a modernized platform versus incremental improvements. Although an agile process could have reproduced many existing functionalities very quickly, we found that certain signal systems employees had the skills to continue to improve the legacy system, access to the source code, and compilers continued to be supported by the vendor. For all those reasons, we provided project management service to deliver the required improvements using the legacy platform. The second one is used by field supervision to record overtime approvals and provide audit compliance. We worked with subject matter experts, field supervision, and executive groups to determine system requirements and develop a process that captured all necessary information without introducing undue burden on supervisory personnel. The completed project plan was turned over to corporate I.T. and compliance groups for implementation.
New Start Commuter Rail Feasibility Studies
O n behalf of numerous clients, we conducted pre-feasibility and feasibility studies on designated rail corridors of starting or reinstating commuter rail service. Typically a project would include:
n behalf of numerous clients, we conducted pre-feasibility and feasibility studies on designated rail corridors of starting or reinstating commuter rail service. Typically a project would include:
- desktop exercise in ridership and revenue forecasting based on U.S. Census and other existing locally available data,
- defining a number of commuter rail alternatives in terms of service levels, station sites, technology, and other pertinent variables,
- order-of-magnitude estimate of required capital investment and a sketch level program based on field factfinding, and any existing infrastructure data provided by partner railroads,
- operating and maintenance cost estimate based on the service and infrastructure requirements, and prevailing rates of railway labour in the local area,
- sketch level service plan, including forecast journey times, schedules, vehicle cycles, and maintenance windows,
- assessment of local transport alternatives, including highway and other public transit options,
- review of existing local growth plans, commercial development strategy, to identify transit-supportive elements,
- preliminary review of real estate in the corridor to identify any potential acquisition difficulties, e.g. for parking,
- strategic overall assessment of likelihood in securing outside funding to initiate the capital investment scheme.
Note: Alex Lu performed this work as an employee of another firm.
Transit Plan for Major Property Redevelopment
 On behalf of a major institutional developer, we worked with a team of consultants to develop a custom trip generation and modal split model to predict the traffic and transit impacts of building out a 9.5 million square feet development over the next 30-50 years on the site of an existing freight rail yard and nearby underutilized sites. The developer’s stated goal was to minimize the automobile traffic impacts by diverting as much of the trips to transit as possible, and to convert some of these commuting trips to internal trips by building housing on-site and providing transit subsidies in lieu of parking spaces. We developed a number of scenarios based on the existing masterplan, developer’s inputs, and various assumptions about economic growth and the timing and programming of major construction projects. For some scenarios, we developed a detailed public transit plan, including projections on where within the metro area the development is likely to attract commuter and non-commuter trips, how these trips are best served by both existing public transit options and future transit investments that may progress independently of this development. Additionally, we developed proposals for re-routing of existing public bus routes and entirely new private bus shuttles that would serve this development, which would connect this area to the rest of the city.
On behalf of a major institutional developer, we worked with a team of consultants to develop a custom trip generation and modal split model to predict the traffic and transit impacts of building out a 9.5 million square feet development over the next 30-50 years on the site of an existing freight rail yard and nearby underutilized sites. The developer’s stated goal was to minimize the automobile traffic impacts by diverting as much of the trips to transit as possible, and to convert some of these commuting trips to internal trips by building housing on-site and providing transit subsidies in lieu of parking spaces. We developed a number of scenarios based on the existing masterplan, developer’s inputs, and various assumptions about economic growth and the timing and programming of major construction projects. For some scenarios, we developed a detailed public transit plan, including projections on where within the metro area the development is likely to attract commuter and non-commuter trips, how these trips are best served by both existing public transit options and future transit investments that may progress independently of this development. Additionally, we developed proposals for re-routing of existing public bus routes and entirely new private bus shuttles that would serve this development, which would connect this area to the rest of the city.
Note: Alex Lu performed this work as an employee of another firm.
Design Charrettes for Rail Operations Support Application
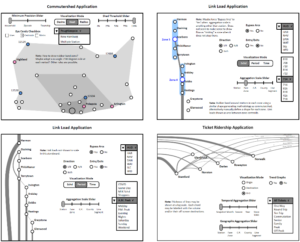 On behalf of a commuter rail agency, we provided a number of concepts and design storyboards for internal-facing operations application, and ran a series of design workshops. Some charrettes were intended to refine the user-interface design, workflow, and required business processes, whilst others were to improve buy-in amongst intended user base for a new or revised application. In all cases, we worked closely with the target user groups to ensure their concerns were addressed, and their business needs were accurately captured in the application design. For some applications, the design concepts were captured in a request for proposal (RFP) which were advertised by the agency in an open solicitation process; for others the designs needed to be fully defined to allow an in-house I.T. team to implement. The various applications we worked on include:
On behalf of a commuter rail agency, we provided a number of concepts and design storyboards for internal-facing operations application, and ran a series of design workshops. Some charrettes were intended to refine the user-interface design, workflow, and required business processes, whilst others were to improve buy-in amongst intended user base for a new or revised application. In all cases, we worked closely with the target user groups to ensure their concerns were addressed, and their business needs were accurately captured in the application design. For some applications, the design concepts were captured in a request for proposal (RFP) which were advertised by the agency in an open solicitation process; for others the designs needed to be fully defined to allow an in-house I.T. team to implement. The various applications we worked on include:
- internal train-tracking application for use by customer service representatives and operations supervisors,
- real estate transaction database application for use by engineering and legal personnel,
- capital as-built drawing filing system for use by capital program and maintenance of way (MOW) engineers, and
- ridership visualization application for use by operations planning and supervisory personnel.
Freight Traffic Diversion Impact Studies

For a variety of clients in both public and private sectors, we performed freight diversion studies that forecast the change in traffic volumes as a result of freight policy or highway infrastructure changes. The studies typically started with locally provided data, specifically some measures of AADTT (annual average daily truck traffic), which we would match against the traffic demands implied by a proprietary origin-destination (O/D) commodity flow database. Having determined the likely O/D and commodities of the traffic mix using the highway facility, we now have much more information about the freight that’s moving on the facility (in key variables such as equipment type, commodity value, sensitivity to route or modal diversion, travel time, toll and labor costs, etc.), and thus could predict with some certainty the likely impact of facility upgrades, engineering alternatives, or policy changes such as time-of-day restrictions or addition of toll lanes. The outputs would include forecast AADTT, revenues, economic impacts, and levels of environmental impacts where this was applicable. Typically we would analyze the traffic impact of several scenarios that included both variables that the client can control, as well as ones that they cannot (such as future economic conditions.) We provided this information to the client who utilizes these results to evaluate their proposed infrastructure investment projects, private investment schemes, or make decisions on freight policy changes in the region.
Note: Alex Lu performed this work as an employee of another firm.
Route Strategies for National Rail Infrastructure Operator
 For a national rail infrastructure owner and operator, we provided analytical support to ascertain the various (route capability, route capacity, and journey time) impacts of investment in rail infrastructure on train operations. Our primary tasks included calibrating a sketch-level train-performance model using field-collected data and limited outputs from a more expensive engineering model; interpreting prevailing signalling rules and achieving an understanding of existing hardware to ascertain maximum practical and theoretical line capacity; conceptual design of alternatives for infrastructure alterations to relieve identified bottlenecks; and cash flow analyses to ensure that the proposed enhancement schemes fit within the envelope of available budget. Some of the ideas we identified have resulted in investment, although not always in the form initially envisaged. The strategic route investment planning process continues on a cyclical five-year basis.
For a national rail infrastructure owner and operator, we provided analytical support to ascertain the various (route capability, route capacity, and journey time) impacts of investment in rail infrastructure on train operations. Our primary tasks included calibrating a sketch-level train-performance model using field-collected data and limited outputs from a more expensive engineering model; interpreting prevailing signalling rules and achieving an understanding of existing hardware to ascertain maximum practical and theoretical line capacity; conceptual design of alternatives for infrastructure alterations to relieve identified bottlenecks; and cash flow analyses to ensure that the proposed enhancement schemes fit within the envelope of available budget. Some of the ideas we identified have resulted in investment, although not always in the form initially envisaged. The strategic route investment planning process continues on a cyclical five-year basis.
Related Publications/Presentations:
- Network Management Statement (incorporating Route Strategy for Scotland Zone)
